Case Report
Management of Cirrhosis – The Basics

Teaching Point
- Common etiologies
- Alcohol
- Hepatitis C and B
- NAFLD
- Complications
- Ascites: spironolactone 100mg/lasix 40mg
- SBP: ceftriaxone 2gm IV q24h
- Hepatic encephalopathy: lactulose, neomycin/rifaximin
Intern Case Conference – Acute Coronary Syndrome
Here is the powerpoint for today's intern case conference on ACS: InternReport.ACS Guidelines: AHA/ACC Guideline for the Management of Patients With Non-ST-Elevation Acute Coronary Syndromes ACCF/AHA Guideline for the Management of ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction Further Reading: Mechanisms of ACS and their…
Drug-Induced Liver Injury

Thank you Dr. Reynolds for an excellent presentation on drug-induced liver injury
Teaching Points
- Patterns of abnormal LFTS
- Hepatocellular: high AST/ALT w/mild elevation in alk phos
- Cholestatic: High alk phos w/ mild AST/ALT
- Causes of hepatocellular injurry
- Alcohol: AST elevation greater than ALT
- Viral: ALT elevation greater than AST
- NAFLD/NASH: AST to ALT ratio typically 1
- Toxins: NSAIDS, abx, statins, anti-epileptic drugs
- Hereditary/autoimmune: hemochromatosis, autoimmune hepatitis, alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency, Wilson’s disease
- Shock: high elevations in AST/ALT
- Non-hepatic causes: muscle disorders, thyroid issues, celiac disease, adrenal insufficiency, anorexia
Atrial Fibrillation
Thank you Dr. Feng for an excellent presentation on the management of atrial fibrillation in the setting of acute de-compensated heart failure
Teaching Points
- Important components of management: hemodynamic stability, rate control, anti-coagulation
- Rate control agents: beta blockers, calcium channel blockers (not preferred in HF), digoxin and amiodarone (also an anti-arrhythmic)
- Antiarrhythmics for afib are Class IC or III
- IC: flecainide, propafeonone
- III: amiodarone, dronedarone, sotalol, dofetilide
- Anti-coagulation: indicated if CHADSVASc ≥ 2 (warfarin or newer agents, ie apixaban or rivaroxaban)
Intern Case Conference 7.6.16
Here is the power point from today’s case conference on the diagnosis and management of Community Acquired Pneumonia. Intern Report 7.6.16
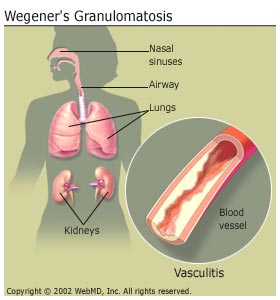
Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis Glomerulonephritis
Thank you Dr. Jang for an excellent presentation on granulomatosis with polyangiitis presenting as lower extremity edema from renal involvement. Teaching Points: GPA can involve multiple organs including nasal ulcers, cartiglage destruction, tracheal stenosis, alveolar hemorrhage, glomerulonephritis, leukoclastic angiitis Diagnosis…
Intern Case Conference 6.29.15
Here is the power point from today’s case conference focusing on the landmark trials that guide our management of CHF.
Ischemic Stroke From Infective Endocarditis
Thank you Dr. Tu for an excellent presentation of ischemic stroke due to septic emboli from infective endocarditis Teaching Points: CNS complications of infective endocarditis can occur in 20-40% patients Etiology: occlusion of cerebral arteries by septic emboli, cerebral hemorrhage, meningitis,…
Progression of Myocardial Infarction
Thank you Dr. Janoian for a great presentation on the progression of myocardial infarction. Teaching Points: pathologic outcomes of MI: arrhythmia, ischemic cardiomyopathy with or without cardiogenic shock, mechanical dysfunction/complications, pericarditis mechanical complications: papillary muscle rupture, ventricular free wall rupture,…
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy/Dysplasia
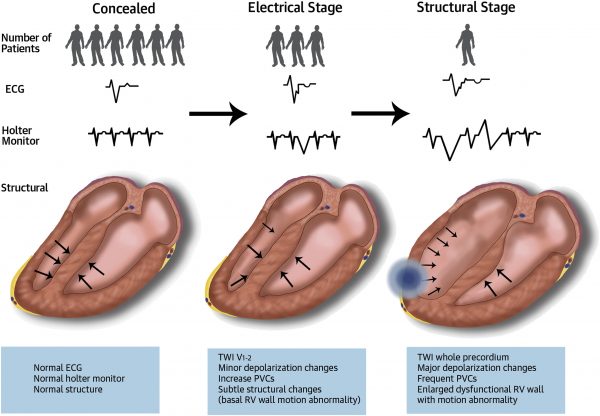
Thank you Dr. Layoun for an excellent presentation on arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy/dysplasia
Teaching Points:
- ARVD is a genetic cardiomyopathy with mutations in desmoglein-2, desmoplakin, desmocollin-2, plakophilin, etc
- Characterized by life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias (monomorphic VT)
- ECG: QRS prolongation (in right precordial leads), RBBB morphology, Epsilon Wave (distinct wave between QRS and T waves, seen in precordial leads, V1 is the best spot)
- Treatment: refrain from high intensity exercise, low dose beta-blocker, ICD for secondary prophylaxis in patients with history of VT or VF
Case Report Archives
- 2020-2021 Academic Year
- June 2021 (12)
- November 2020 (1)
- October 2020 (1)
- August 2020 (1)
- 2019-2020 Academic Year
- June 2020 (10)
- May 2020 (4)
- April 2020 (1)
- March 2020 (1)
- February 2020 (1)
- January 2020 (3)
- November 2019 (3)
- October 2019 (2)
- September 2019 (3)
- August 2019 (4)
- July 2019 (10)
- June 2019 (1)
- 2018-2019 Academic Year
- June 2019 (1)
- May 2019 (5)
- April 2019 (2)
- March 2019 (3)
- February 2019 (2)
- January 2019 (2)
- December 2018 (1)
- November 2018 (1)
- October 2018 (4)
- September 2018 (3)
- August 2018 (8)
- July 2018 (3)
- 2017-2018 Academic Year
- June 2018 (3)
- May 2018 (4)
- April 2018 (3)
- March 2018 (4)
- February 2018 (3)
- January 2018 (2)
- December 2017 (2)
- November 2017 (5)
- October 2017 (5)
- September 2017 (12)
- August 2017 (11)
- July 2017 (4)
- 2016-2017 Academic Year
- June 2017 (1)
- May 2017 (2)
- April 2017 (2)
- March 2017 (3)
- February 2017 (2)
- January 2017 (2)
- October 2016 (2)
- September 2016 (5)
- August 2016 (3)
- July 2016 (7)
- June 2016 (1)
- 2015-2016 Academic Year
- June 2016 (3)
- March 2016 (2)
- January 2016 (4)
- December 2015 (6)
- November 2015 (3)
- October 2015 (10)
- September 2015 (7)
- August 2015 (11)
- July 2015 (12)
- June 2015 (1)
- 2014-2015 Academic Year